Use Cases
We will continuously add new use cases here. If you need help configuring rules for a specific case, please provide feedback, and we can add it.
Ransomware Protection
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that specifically encrypts files. Since its operational behavior is similar to some normal software, making it difficult to detect. It can be achieved through the following methods for ransomware defense.
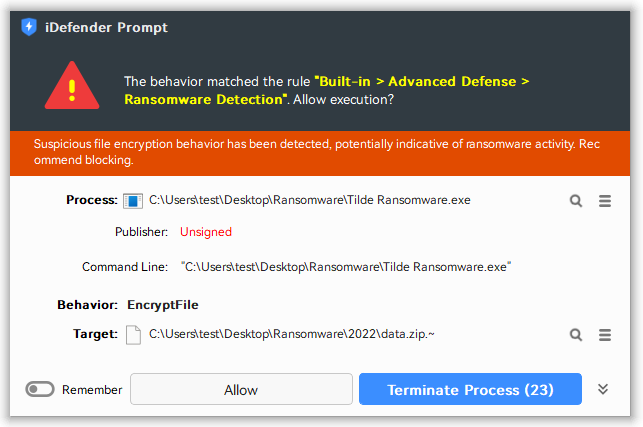
Method 1: Encryption Behavior Detection Based on Entropy Increase Principle
Ransomware Detection in the built-in rule, by monitoring entropy changes during file encryption and combining this with other typical file manipulation signatures of ransomware, it can effectively identify most known ransomware. However, this method cannot guarantee a 100% detection rate and requires continuous optimization to protect against more viruses.
If you have any undetected malware samples, please submit them to us for analysis. We will add detection capabilities based on our findings.
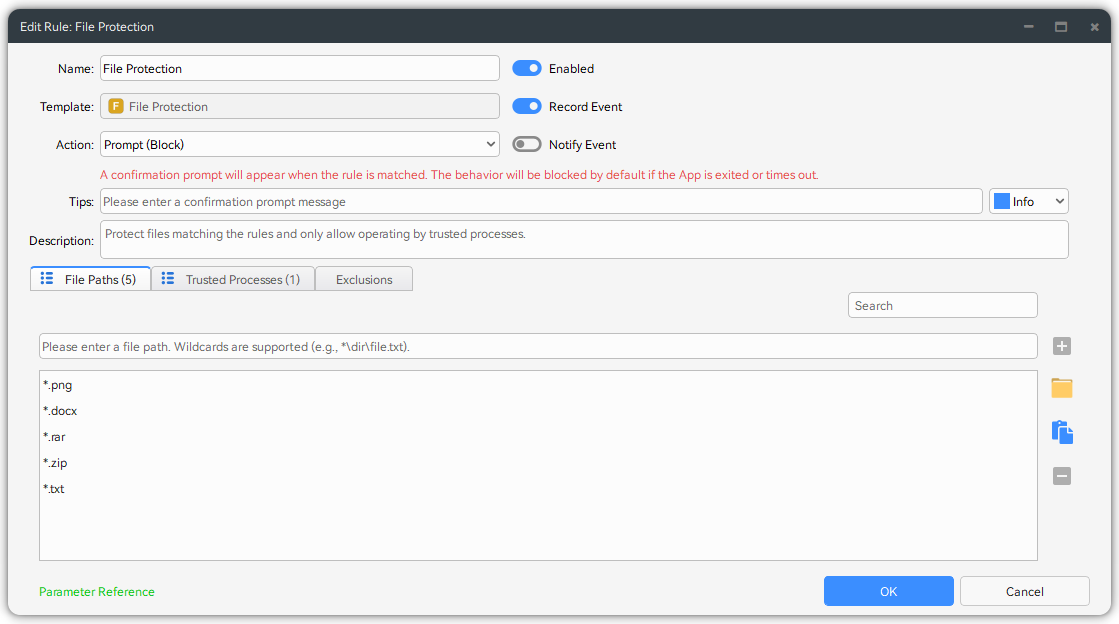
Method 2: Protect via File Protection Template
Configure the File Protection rules, specify the file extensions that need protection (such as .docx, .xlsx, etc.), and define trusted processes (such as Office applications) allowed to access these files. When an unknown process attempts to modify protected files, the a prompt dialog will appear, allowing you to choose whether to trust or block based on your assessment, and subsequent identical behaviors will not be prompted again. This method can directly prevent unauthorized file tampering.
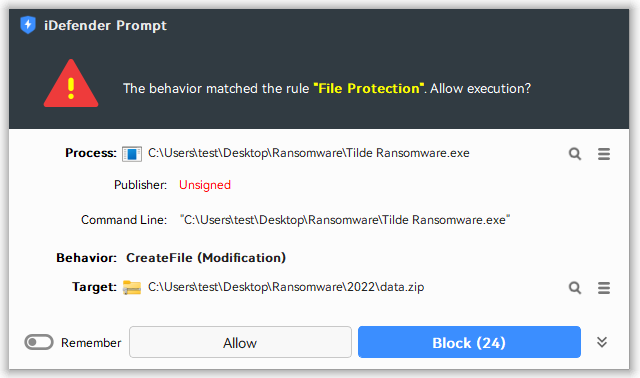
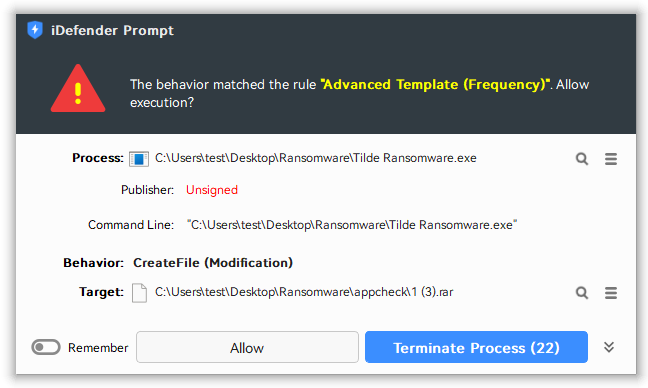
Method 3: Behavior Detection Based on High-Frequency File Operations
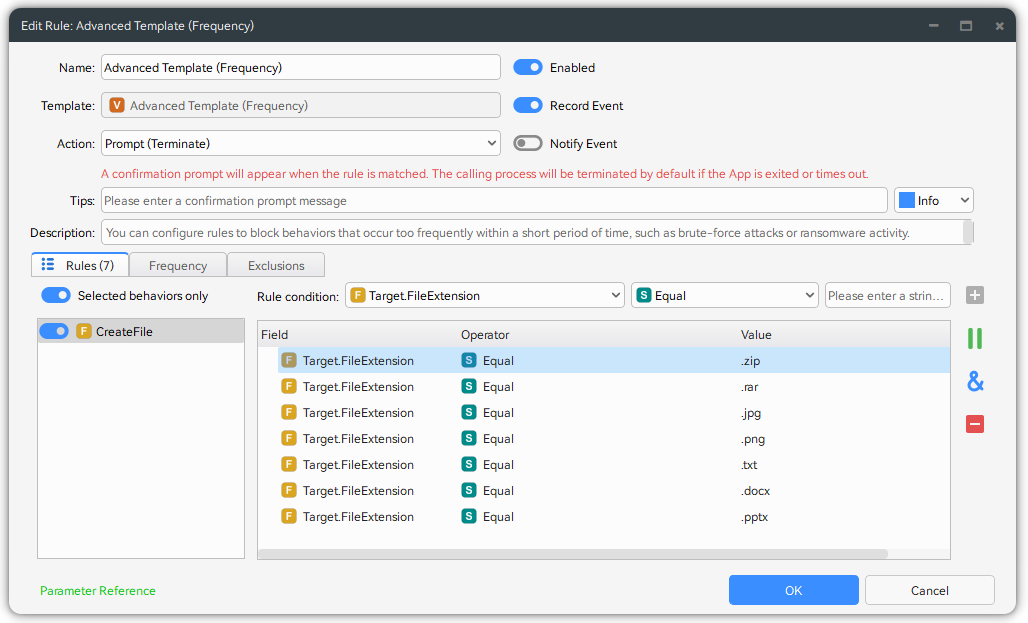
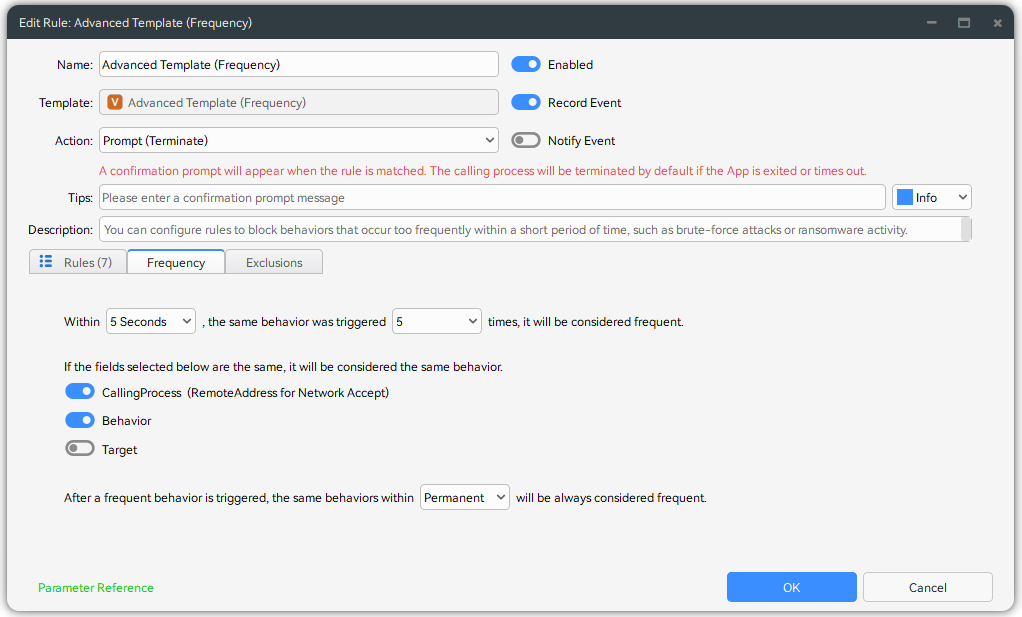
Configure the Advanced Template (Frequency) rules, set rules to monitor frequent modifications of multiple files within a short period (e.g., more than 5 files modified within 5 seconds). Such abnormal behavior usually indicates that ransomware is performing batch file encryption, and triggering the rule allows timely attack blocking.
Information Stealing Protection
Info-stealing malware harvests sensitive data from browsers (such as saved passwords and cookies), as well as from other system areas like local files, email clients, and instant messaging applications.
You can configure Block File Access or Block File Access (Kernel) rules to block malicious processes from accessing sensitive files, thereby achieving info-stealing protection.
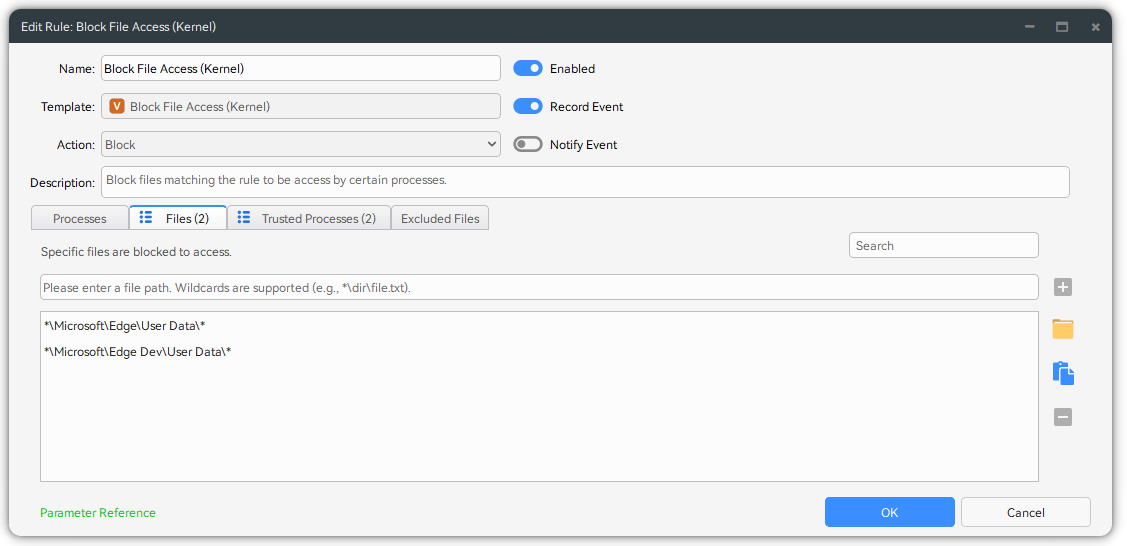
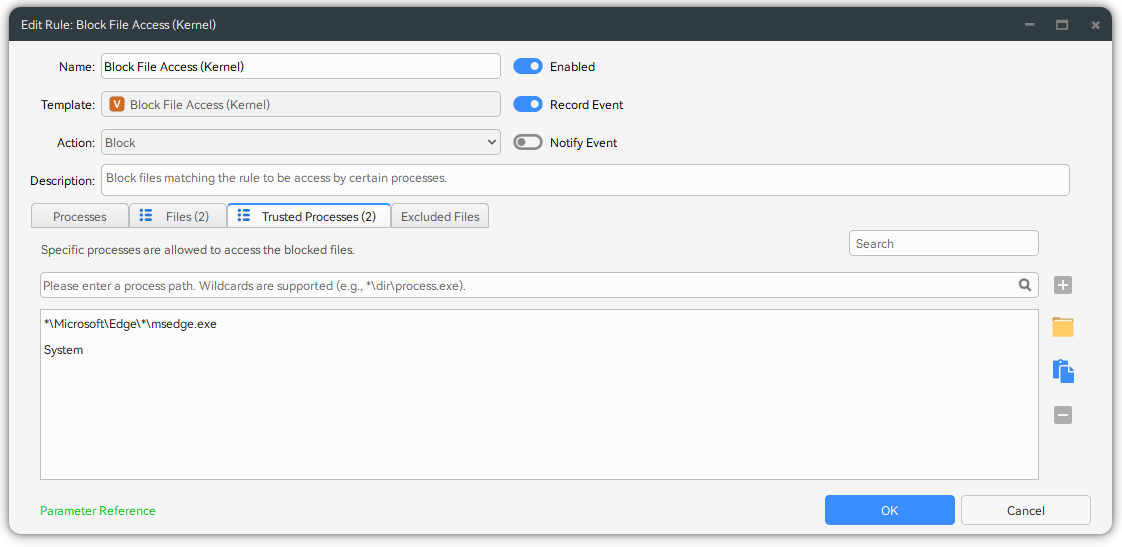
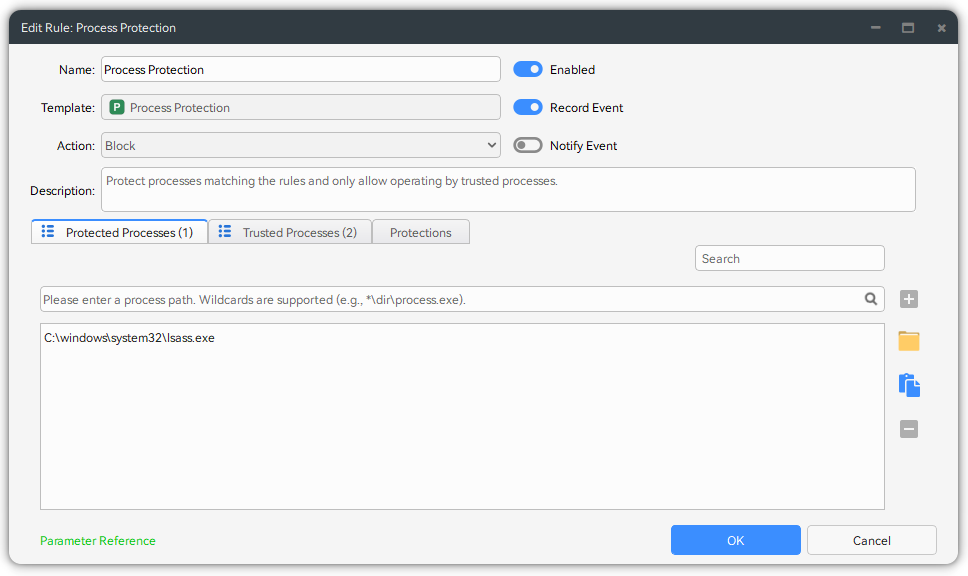
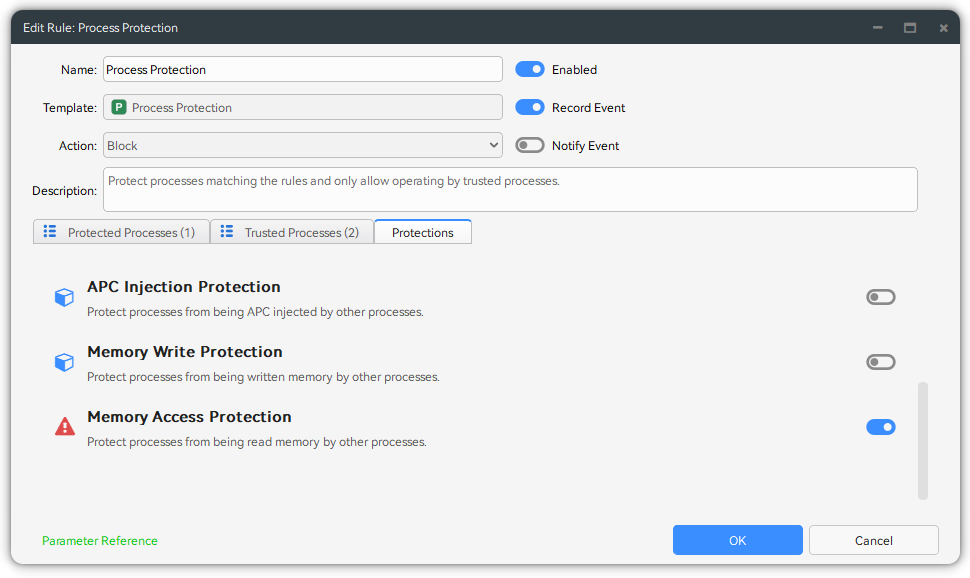
Credential Dumping Protection
Malware or stealing tools extract login credentials stored in process memory by reading the memory of lsass.exe or generating its dump file. Such attack behavior falls under credential access techniques.
You can configure Process Protection rule to intercept illegal read operations targeting lsass.exe can effectively block such attacks.